WHY CHOOSE US?
Our mine is a trusted source of high-grade Zeolite
Art Of Mining Techniques
Environmentally Responsible
Industry Leader
Trusted Expertise
How Does Zeolite Work?
Zeolite works through a process called adsorption. It has a unique porous structure that allows it to attract and trap certain molecules. The internal structure of natural zeolites is composed of large channels and cages containing H2O molecules and cations such as K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+. These molecules and cations can ionically exchange with other elements. When zeolite comes into contact with substances like odors, toxins, or heavy metals, it selectively adsorbs and binds to these molecules, removing them from the surrounding environment. This adsorption process is facilitated by the specific composition and structure of zeolite, which provides a large surface area for capturing and holding onto molecules. As a result, zeolite can effectively purify water, control odors, and help in various industrial and agricultural applications. Its adsorption capabilities make it a versatile and valuable material in addressing environmental and industrial challenges.
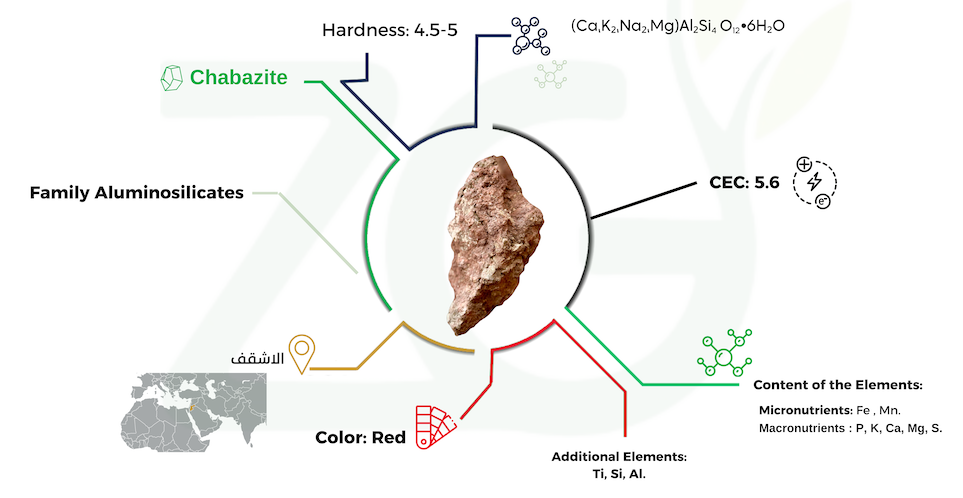
Chabazite Properties
Hardness
Chabazite exhibits a hardness of 4.5 to 5 on the Mohs scale, indicating its relatively soft nature.
Specific gravity
The specific gravity of chabazite falls within the range of 2.0 to 2.2, indicating its relatively low density compared to other minerals.
Crystal structure
Chabazite possesses a complex crystal structure characterized by interconnected cavities and channels. These channels can trap and release molecules, such as water, gases, and cations.
Ion exchange capacity (IEC):
Chabazite exhibits a high ion exchange capacity due to its porous nature and the ability to trap cations within its structure. This property is valuable for various applications, such as hard water and wastewater treatment.
Porosity
As a highly porous mineral, chabazite exhibits excellent adsorption and desorption properties. This characteristic makes it well-suited for various applications, including gas separation and ion exchange processes, where efficient molecule trapping and release are essential.
Thermal stability
Chabazite exhibits excellent thermal stability, enabling it to withstand high temperatures without significantly changing its structure or properties.
Optical properties
Chabazite possesses a refractive index ranging from 1.478 to 1.490 and a birefringence of 0.005 to 0.008. These properties make it useful in optical applications such as microscopy and polarizing filters.
Chemical reaction
Chabazite has high chemical reactivity and can catalyze chemical reactions, particularly in converting natural gas liquids into gaseous forms.
Occurrence
Chabazite is relatively rare and is primarily found in volcanic rocks, particularly within cavities and fractures of basaltic and andesitic lava flows.
Adsorption
Chabazite exhibits excellent adsorption properties, making it valuable in gas storage, purification, and catalysis applications by adsorbing molecules onto its surface, especially in gas-phase reactions.
Surface Area
Chabazite possesses a relatively high surface area, facilitating interactions with numerous molecules. This property finds utility in applications such as adsorption, catalysis, and molecular separation.
Stability
Chabazite demonstrates excellent stability both in terms of its chemical and physical properties, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
Shape selectivity
Due to its complex 3D structure with interconnected channels and cavities, chabazite exhibits shape-selective properties, enabling it to be employed in shape-selective catalysis and molecular sieving.
Selectivity
Chabazite exhibits high selectivity towards specific molecules, allowing it to adsorb or trap certain molecules while excluding others selectively. This property finds applications in gas separation, water purification, and ion exchange processes.
Why Zeolite (Chabazite)?
Natural Origin
Zeolite is an extraordinary mineral that arises from the dynamic interplay of volcanic activity and the interaction of water with volcanic ash or lava. Zeolite crystals emerge through a gradual process of chemical reactions between volcanic materials and groundwater or seawater, showcasing their distinctive porous structure comprising interconnected channels and cavities. With deposits sourced globally, including volcanic regions and sedimentary formations, Zeolite stands as a natural mineral of unparalleled significance. Its innate formation imbues Zeolite with a remarkable surface area and porosity, rendering it invaluable for many applications.
Chabazite, a sought-after type of Zeolite, is meticulously extracted from our mine in the northern Jordan region. We carefully mine this mineral from our abundant deposits, paying close attention to detail. Chabazite’s unique crystal structure and pseudo-cubic shape hold great potential. It possesses impressive properties such as high porosity and ion exchange capacity, and chabazite holds immense value across various industries. We ensure a reliable supply of this exceptional mineral by sourcing chabazite from our Jordanian mine. This enables us to deliver unparalleled quality products to meet the diverse needs of our valued clients.
Mineral Content
Our Zeolite predominantly comprises 90% chabazite, with the remaining 10% comprising other types, such as phillipsite and faujasite. This unique mineral content sets it apart, with a maximum silica content of 41%, which is relatively low compared to other zeolite types. It contains 51% of the crucial elements necessary for optimal plant growth. Among these elements, 45% is attributed to chabazite, while the remaining 6% comprises the other types (phillipsite and faujasite). Additionally, our chabazite exhibits a rich Fe2O3 content, reaching 10.2%. This substantial iron oxide content contributes to the distinctive red coloration observed in our specific variety of chabazite. Furthermore, our Zeolite maintains a sodium content of no more than 1.1%, demonstrating its comparably low levels when contrasted with other zeolite types.
Sustainability
Chabazite demonstrates commendable sustainability through its unique properties and applications. Its exceptional adsorption capacity contributes to environmental sustainability by effectively removing pollutants, contaminants, and harmful substances from various mediums, such as air and water. This capability aids in mitigating pollution and improving overall air and water quality.
Chabazite’s sustainable impact is further highlighted in its use in water treatment, where it efficiently removes heavy metals, organic compounds, radioactive contaminants, and other impurities, promoting clean and safe water supplies. Moreover, chabazite’s moisture and nutrient retention properties make it valuable in agriculture, reducing the need for excessive watering and fertilizing, thus promoting responsible management. By enhancing nutrient availability and water retention, chabazite helps plants develop stronger root systems and withstand environmental stresses, reducing the need for excessive pesticide applications. This reduction in pesticide use promotes environmentally friendly farming practices, protects beneficial organisms, and contributes to the preservation of ecosystems. Chabazite plays a crucial role in sustainable practices, environmental protection, and pursuing a more sustainable future through its multifaceted contributions.
